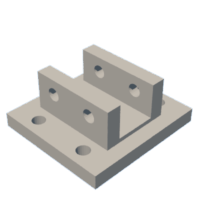
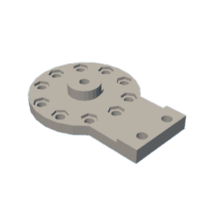
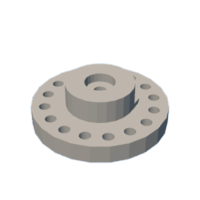
Introduction: Magnetic Gear Box
This can be used to gear down or gear up the output shaft's rpm compared to input shaft's rpm.
There are (16) - 8mm x 10mm magnets on the input side. (8 Pole Pairs)
And (4) - 32mm x 3mm Magnets on output side.(2 Pole Pairs)
Magnets : (16/4 = 4) or Pole Pairs : (8/2 = 4)
This will give a 1 to 4 ratio. between the 2 shafts. (Step up or Step down)
The rotation direction of the output shaft can be changed with the number of pole pairs used.
An odd number of pole pairs (N&S) will give same direction of input and output shafts
An even number of pole pairs (N&S) will reverse output shaft direction vs input shaft.
CAUTION: If you use rare earth super strong Neodymium Disk Magnets.
These can be dangerous use proper care when using them.
I have not experimented with refrigerator magnets, so I don't know how they would preform.
To calculate the number of bolts needed for center ring/stand
Add the number of magnets used and divide the total by 2
this model (16+4 = 20) / 2 = 10 bolts
or add the number of pole pairs 8+2 = 10 bolts
(16+6 = 22/2 = 11 bolts (the 10 bolts work but will experiment to see if 11 is better/worse.)
or add the number of pole pairs 8+3 = 11 bolts
Attachments
Supplies
- 3d printer
- PLA filament was used to print parts
- 10 M8-1.25 x 25mm full Threaded Hex Bolts
- 10 M8-1.25 Hex Nuts for nut stand
- 2 : M8-1.25 x 60mm full threaded Hex Bolts
- 1 : M8 x 150mm Aluminum tube or shaft.
- 2 : M8 Collars ( optional )
- 10 M8-1.25 Nuts
- 4 : M8 Nylon or Printed Flat Washers (extras may be used for correct clearance)
- 16: 8mm x 10mm Magnets (Rare Earth Magnets used in this demonstration)
- 4 : 32mm x 3mm (Rare Earth Magnets used in this demonstration)
- 6 : 32mm x 3mm Magnets (Rare Earth Magnets for extra experimenting).
- Glue / double stick tape optional
Optional build:
The structure can also be made from other material (wood,plastic,cardboard, etc.)
1 needed: 16 magnet ring is 100mm Diameter
center of magnets are 40mm radius from center or ring @ 22.5 degrees from each other.
2 needed: Center stand is is 100mm Diameter
center of bolts are 40mm radius from center of circle @ 36degrees from each other.
1 needed: 4 magnet ring is 120mm Diameter
center of magnets are 40mm radius from center of ring @ 90 degrees from each other.
Step 1: 3D Printed Parts
Print 1 each of the following files:
Printed at 20% infill
No extra support is required. (already built into files that need support.)
- Base_For_Bolt-Nut_Stand
- Large_magnet_Ring_4_Mag_32mm_with_Bearings
- Small_Magnet_Ring_16_Mag_with_Bearings
- Stand_For_Bolts_No_Bearings
- Stand_For_Nuts_No_Bearings
- 608_Bearing_Replacement
- For extra experimenting if wanted:
- Large_Magnet_Ring_6_Mag._32mm_with_Bearings
- this has 6 magnets making a 3 pole pair. (same rotation)
Remove all Support structure where it was used (not much used)
Attachments
Step 2: Assembly
Clean / and remove the support material from printed parts.
Press and / or glue the magnets in to the Magnet rings.
Alternate "North" then "South "then "North" then "South"... etc.
Check polarity of magnets as you install them.
Bolt the Bolt Stand and Nut Stand together Flat side facing each other.
Using 16 M8-1.25 x 25mm Hex Bolts and M8-1.25 nuts.
install a M8-150 mm Aluminum shaft or tube through the stand. assembled bolt/nut stands.
Attach the base to assembled Stands and secure with 2 M8-60mm hex bolts.
With magnets and bolts in place & tightened , slide a magnet ring on one side,
check for clearance between Stand and Ring.
The Magnet Ring should rotate freely. If not, you may need to add another washer.
Install a 8mm collar on each side of aluminum shaft if using.
Step 3: Testing
This will demonstrate how the magnetic gear box works:
Step-Up gear box:: 1 turn of the small ring (Yellow) will turn the large ring (Blue) 4 times , Opposite direction
Step-Down gear box:: 4 turns of the large ring (Blue) will turn of the small ring (Yellow) 1 time, Opposite direction
Removing the Large_magnet_Ring_4_Mag and install the Large_Magnet_Ring_6_Mag.
Now you have 8 pole pairs on input ring and 3 pole pairs on output = 11 pole pairs.
Step-Up gear box:: 1 turn of the small ring (Yellow) will turn the large ring (Blue) 4 times , Same direction
Step-Down gear box:: 4 turns of the large ring (Blue) will turn of the small ring (Yellow) 1 time, Same direction
Attachments
Step 4: Pros & Cons
Here are some Pros:
- Change output ratio
- Change Direction
- Disengage Input from Output, Protecting object being powered
- Provide motion to an object in vacuum chamber while supplying motion from outside.
- Clean Room Application.
- Gears / Chains not needed or maintained
- Pulleys / Belts not needed or maintained
- No Friction between magnet rings reduce maintenance
Here are some Cons:
- Output depends on quality of magnets
- Loss of torque (?? don't know how much.)
- May not be cost effective
- Weight may be more.
- Loss of physical contact not good in some applications, (elevator / Winch etc..)
Closing Thoughts / Questions
Google Magnetic Gear Box or Magnetic Drive for more info. & Videos.
I am researching this to use in a small multi-vertical Wind Turbine Project .
I have seen Videos of this design spinning the output shaft at 10,000+
but this was a slow increase in speed.
Will guests of wind cause generator unwanted disengagement?
This type of gearbox is not a fit all but it may work better in some applications.
The low speed input with higher output will be great.
Automatic clutch to disengage Generator (protecting it)
I don't know the amount of torque loss for operating the generator.
Would bar magnets be a preform better? What size?
Your comments and suggestions are welcome.
Thank You for your time.

Participated in the
Make it Move Challenge